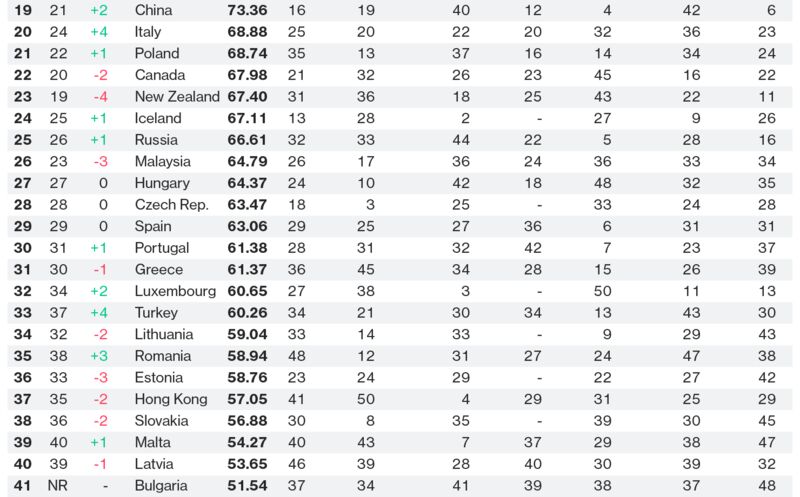
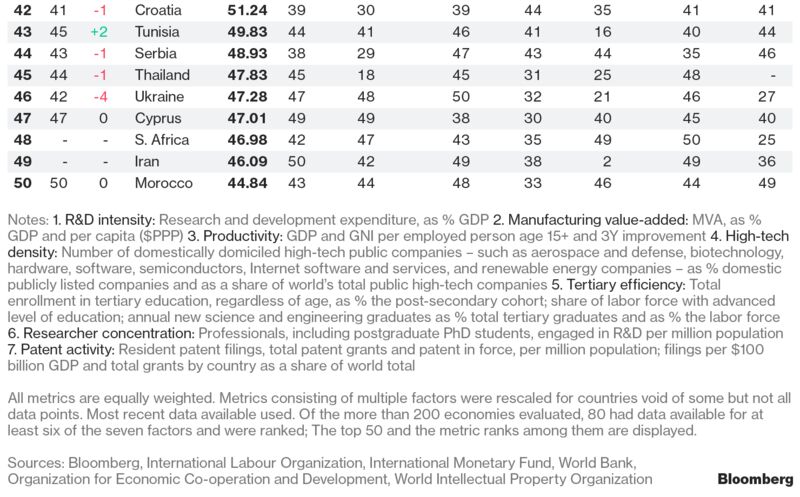
Predicting the Long-Term Future – 2043, 2118, and 2218
Tomado de: Fast future publishing, https://us10.campaign-archive.com/?u=b2bac6b3fa5b485c0809f5c81&id=b937ebb586 or http://mailchi.mp/fastfuturepublishing.com/2018-12gdpr, 04/06/2018
The team at Fast Future have been doing an exercise to envisage scenarios of what our world might look 25, 100, and 200 years into the future. Here are the outcomes. We’d welcome your thoughts on these scenarios, and your own views on how our world might play out.
2043: How the world might look in 25 years

Artificial living – artificial intelligence (AI) will permeate our world. The technology will be in use across every aspect of society from healthcare and education to entertainment and financial services. Smart systems could manage our social lives, help us select the ideal partners for dating, marriage, and reproduction, monitor our health in liaison with our doctors, and personalise our education so content is delivered in the way we learn best. The technology will be making legal decisions in court, determining our benefit payments, fact checking politicians, and powering the transport sector.
Smarter money – By combining the power of AI and blockchain, the concept of money could evolve into electronic tokens with far more types of assets tradeable within the one “currency”. For example, we might earn tokens from our employment, as rewards from retailers and airlines, and as micro-credits for completing workplace training or school learning tasks. Instead of simply liking a track from a musician, we could now make a micro-payment to them with a fraction of a token. This evolution from cash and cryptocurrencies towards a universal means of exchange could mean the end of cash and foreign exchange markets.
Rohit Talwar, CEO, Fast Future

Autonomous city centers – Following a widely invoked policy to ban petrol and diesel fuelled vehicles from city centers, the same happened with manually driven cars. An era marked by exponential change has seen changing ideas of asset ownership, radical leaps forward in AI, increasingly efficient electric propulsion units for vehicles, and the emergence of smart city infrastructures. These relatively smooth transitions led to other changes in cities, including the removal of redundant traffic signals and the remodelling of some street intersections.
Autonomous cargo aircraft – While most passengers are sceptical about an autonomous plane ride to their destination in the sun, cargo has no such qualms. While regulations allow the operation of autonomous aircraft for cargo purposes, they are still operated between specialist cargo hub airports, separate from passenger traffic.

Autonomous commuter trains – Overground and subway / metro commuter services are now fully automated in many cities. At busier stations and at peak travel times, train staff supervise the safety of passengers at the station, but the trains themselves are fully autonomous with AI systems driving the train and monitoring passengers. As yet, long distance express trains retain on board crews, although much like civilian aircraft, the drivers’ roles are to supervise the systems and provide on board customer service.
The first 3D printed Moonbase – Following a series of missions to create an autonomous 3D accommodation manufacturing facility on the Moon’s surface, the facility is now ready. The Moonbase will support greater and more extensive autonomous and human exploration of the Moon’s surface and serve as a base for onward missions to deep space.
Steve Wells, COO, Fast Future

Food revolution – Within next 25 year every aspect of the life we know will change. The way we produce our food will change. Fruits and vegetables might be grown in buildings controlled by AI rather than on farms, meat could be cloned, and we might see widespread consumption of 3D printed food.
Asia rising – Looking at the development of the Asian market, is reasonable to expect that within 25 years world economic and industrial leadership will have passed to China and India. The growth of China and other Asian economies will continue to outstrip more developed nations as see Asian nations as the driving force of the world economy rather than the USA and European countries.
Karolina Dolatowska, Researcher, Fast Future

Agricultural disruption – The food chain will undergo a major transformation led by AI, vertical farming and lab grown meat. Hydroponics plants, fruits, and vegetable might change agriculture as we know it, and help revolutionize the food industry. Overpopulation is having major consequences, driving a lack of growing space and food in many parts of the world. The growing global population will force us to find creative solutions. Having AI-controlled hydroponic vertical farms on the sides of buildings might be one of the solutions.
Artificial meat – In-vitro cloned meat could be another future solution to our food supply problems. While lab grown meat may still face many challenges, such as flavour control, it also has many advantages such as less waste, less risk of viruses, reduced space requirements, and lower emissions and environmental impacts among others. These benefits seem to outweigh the disadvantages and drawback of traditionally reared livestock. The idea of artificial meat might disturb us, nonetheless this solution seems to be finding its way into our diets.
Helena Calle, Researcher, Fast Future

Water innovation – As climate change continues to alter rainfall patterns worldwide, water may become an increasingly scarce resource. Regions with the financial capital may be able to invest in the latest microfiltration technologies, thus allowing constant recycling of waste water into drinkable water. Desalination plants may be the solution in arid regions along coastlines. Hopefully, as technology improves, and costs fall, the issues associated with desalination, namely high energy usage and residual salt, could be resolved to such a degree that coastal regions all over the world would be able to afford desalination.
April Koury, Researcher, Fast Future
Artificial wombs – within the next 25 years it may be possible to prevent preterm mortality in infants by use of artificial wombs that provide all the conditions required to safely achieve full development and birth of a foetus. This technology would at first be used to save at-risk pregnancies but may over time become a reproductive technology available to consumers interested in having a baby without pregnancy.
Antibiotic failure – Many pathogens are gaining immunity to the antibiotic medicines available today. Without antibiotics, common illness and medical procedures, even pregnancy and childbirth, could become endangering events. In the next 25 years, is it possible that we will experience «the end of antibiotics» (as the World Health Organization put it in 2016)? Fortunately, the microbial threat is being met with advanced drug development, allowing medical researchers to explore new approaches to fight superbugs. New strategies on the horizon range from genetic modification of germs and implantable semiconductors through to the discovery of new antibacterial agents in soil.
Alexandra Whittington, Foresight Director, Fast Future
2118: How the world might look in 100 years

The world has been transformed by the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), the emergence of artificial superintelligence (ASI), and the reworking of economic and financial systems using distributed technologies such as blockchain. The majority of people now work on a voluntary basis as all their basic needs are catered for by guaranteed incomes and free universal services such as transport, food, education, and utilities. Old notions such as government have been replaced by community decision making and the community at large now owns the intellectual property for all new advances in science and technology. The community is also a 50% shareholder in every business, with the returns reinvested based on priorities set by the community. You can still work if you want to – but no one has a job, we just play various roles in society, and self-organisation by activities is the way most things get done.
Society leads a far more balanced existence on the planet – only using what we need, managing our resources more sustainably. The focus of education is on maximising the individual’s talents and potential, and with lifespans of 150 years or more now routine, there is plenty of time to try our hand at everything we’d like to do. Wealth has been redistributed with a maximum multiple of ten between the assets of the richest and poorest, but most assets are in public ownership. Education centres such as schools, colleges, and universities have become the gathering centre for the community, where anyone can attend free courses, run 24/7/365 and delivered by anyone who has something to say – either in presence or via a variety of electronic delivery services.
Rohit Talwar, CEO, Fast Future
«A world divided between abundance and automation – where technology has been deployed for the good of society; where products and services are basically free across a numbers of linked nation states and trading / political blocks with reasonably successfully harmonised taxation and regulatory systems – and the rest; states initially side-lined as politically and economically incompatible and a number of disparate nation states struggling to make the transition to the «modern» world, and a source of unrest within their own borders and internationally, have basically divided the world in two.
Colonies on the Moon and Mars are beginning to thrive with corporate governance. Given the colonisation – initially through a moon base staging post to Mars – was established by the private sector rather than the state players involved in the 1960’s and 70’s space race, there was little that governments on earth could do other than hang onto their coat tails as the technology developed came through company R&D activities. Both the Moon and Mars became staging posts for autonomous missions deep into the solar system as the search and commercialisation of other planets gathers pace.»
Steve Wells, COO, Fast Future
2218: How the world might look in 200 years

“In 2218 the natural systems of the earth could be well on their way to rebounding from the brink of collapse. If today’s decision-makers choose to put resources toward avoiding ecological collapse (including strict adherence to carbon policies, and full support for development of renewable energy), the world of 2218 might be a more healthy and balanced place where life can be supported for hundreds of years to come. Some scientists, including the late Stephen Hawking, warn that we have 100 years of life left on this planet. Instead of exacerbating the issues for another 100 years, we could solve the problems we have created on earth which threaten life as we know it. If we take that advice today, and begin repairing things now, we may have a very desirable, functional and safe ecosystem for future generations to enjoy. If we do not, I doubt there will be much to see in 2218”
Alexandra Whittington, Foresight Director, Fast Future
Earth has become part of the Inter-Galactic Federation of Planets (IGFP). The period from 2020-2050 saw a series of inter-related and cascading collapses of the economic, trade, financial, political, environmental, and social systems that had previously steered growth and progress. Advances in technologies such as AI had only served to accelerate dysfunctionality and wealth disparity. After the chaos of systemic failure, the planet gradually moved to adopt open, fairer, and more ecologically sound governance practices. As Earth started to establish a new equilibrium, so members of the IGFP started to make contact and introduce us to their values, ways of life, and advanced science and technology. Earth finally joined the IGFP in 2120 after a prolonged period of transition and adjustment.
In 2018, the New Earth now pursues an ecologically sound path and stewardship of the planet is a core part of the education curriculum alongside community engagement and civic responsibility. Abundance has become a reality, money no longer exists as a means of exchange, but citizens can accumulate credits for their acts of learning and service. Credits can be traded for the rights to visit the most distant of planets or to work on the most community focused initiatives. Manufacturing of goods is largely in the hands of technology, and ownership has been replaced by usership, with sharing a key organising principle across society. Everyone can have a say on every issue, and an elected IGFP governance council serves strict two year time limits to steward through the choices made by citizens.
Rohit Talwar, CEO, Fast Future